In the mid-1600s, the Dutch enjoyed a period of unmatched wealth and prosperity (the Dutch Golden Age). Newly independent from Spain, Dutch merchants grew rich on trade through the Dutch East India Company. With money to spend, art and exotica became fashionable collectors items. That’s how the Dutch became fascinated with rare “broken” tulips, bulbs that produced striped and speckled flowers. First these prized tulips were bought as showy display pieces, but it didn’t take long for tulip trading to become a market of its own.
Tulip prices spiked from December 1636 to February 1637 with some of the most prized bulbs, like the coveted Switzer, experiencing a 12-fold price jump, creating the first recorded speculative asset bubble in history, a bubble which popped in February 1637 when the price for tulips collapsed.
In a controversial 1841 publication, Charles Mackay suggests that shock to Dutch commerce caused by the collapse of tulips prices rippled through Western Europe: the first international market crash. Some modern historians contest Mackay’s account, arguing that his research was flawed, but what remains true is that asset price bubbles and subsequent corrections have been around for 400 years and don’t appear to be going away.
In this guest blog by Helen Paul, Lecturer in Economics and Economic History at the University of Southampton (published with thanks under a creative commons license), Helen ‘celebrates’ the 300th anniversary of the South Sea Bubble and the story behind it’s iconic financial crash:
300 years since the South Sea Bubble: the real story behind the iconic financial crash

Wikimedia
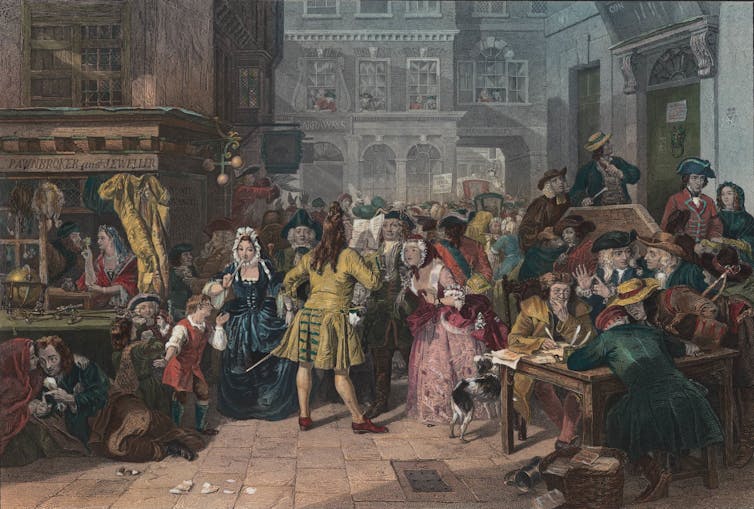
Coronavirus has caused a great deal of stock market turbulence and, somewhat inevitably, comparisons have been made to the volatility caused by the South Sea Bubble 300 years ago. This was the moment when, in 1720, share prices in London boomed and then fell sharply. It is thought of as a major economic disaster and huge scandal.
In reality, it was a scandal but not much of a disaster. While some investors lost out from the speculation, it did not make much of a dent in the wider economy, unlike the more recent crashes of 1929 and 2008 – and what the long-term economic effects will be from COVID-19.
The episode shows how a perceived crisis can be the subject of intense public outcry and moral panic, even when people do not understand what has happened. It shows how the narrative told to the public can easily diverge from the truth: fake news, if you will.
What actually happened
The real reasons behind the bubble are complex. The South Sea Company, which gave its name to the event, helped the government manage its debt and also traded enslaved Africans to the Spanish colonies of the Americas. The government struggled to pay holders of its debt on time and investors had difficulty selling on their debt to others due to legal difficulties.
So debt holders were encouraged to hand their debt instruments to the South Sea Company in exchange for shares. The company would collect an annual interest payment from the government, instead of the government paying out interest to a large number of debt-holders. The company would then pass on the interest payment in the form of dividends, along with profits from its trading arm. Shareholders could easily sell on their shares or simply collect dividends.
The debt management and slaving aspects of the company’s history have often been misunderstood or downplayed. Older accounts state that the company did not actually trade at all. It did. The South Sea Company shipped thousands of people across the Atlantic as slaves, working with an established slave trading company called the Royal African Company. It also received convoy protection from the Royal Navy. Shareholders were interested in the South Sea Company because it was strongly backed by the British state.
By the summer of 1720, South Sea Company shares became overvalued and other companies also saw their share prices increase. This was partly because new investors came into the market and got carried away. In addition, money came in from France. The French economy had undergone a huge set of reforms under the control of a Scottish economist called John Law.
Law’s ideas were ahead of his time, but he moved too quickly. His attempts to modernise France’s economy did not work, partly because the rigid social system remained unchanged. The French stock market boomed and then crashed. Investors took their money out of the Paris market – some moved it to London, helping push up share prices there.
Wikimedia
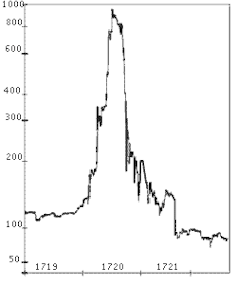
Once the South Sea Bubble had started to inflate, it attracted more naive investors and those who would prey upon them. While it was clear that the high prices were unsustainable, canny speculators bought in hoping to sell out in time. This pushed up prices even more, in the short term. The stock price went up from £100 in 1719 to more than £1,000 by August 1720. The inevitable crash back down to £100 per share by the end of the year came as a shock to those who thought they could make their fortunes overnight.
The backlash
The crash provoked huge public outcry. Politicians demanded an inquiry. South Sea Company directors were accused of treason and fraud. Poems, plays and satirical prints criticised the market and those in it. The chancellor of the exchequer was briefly locked up in the Tower of London. The company’s directors were forced to appear in front of parliament.
The amount of noise generated by these reactions helped make the South Sea Bubble famous. From then on in, it became a byword for financial scandal. Yet many people could not really explain what had happened. Perhaps surprisingly, economic historians can find little evidence of a prolonged economic recession. The bubble burst but without the major effects of later financial crises.

Wikimedia
So why all the fuss? First, the crash happened in the early days of the stock market. There was no body of financial theory or financial journalism which could help explain it to laypeople. They turned instead to conspiracy theories or strange ideas about people becoming gambling mad.
Second, there was talk of people being given their money back. This gave losers every incentive to talk up their losses. It is human nature to complain, even about a small loss. The popular perception is that great fortunes were destroyed, but there is little evidence of this beyond one or two cases.
Third, this was a glorious opportunity for schadenfreude and various sorts of prejudice to be expressed. Female investors were lampooned by misogynists. Foreigners and various religious groups were the subject of racist commentary. There was no expert analysis available and commentators, with no real understanding of finance, provided scandal and scapegoating instead of accurate reporting.
The South Sea Bubble has been a symbol of financial crisis for 300 years. But like other more modern crises, its public image diverges from the reality. The same probably can’t be said for the COVID-19 pandemic, which will have a much more deep and lasting effect on the world economy.![]()
This contributions is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Helen Paul, Lecturer in Economics and Economic History, University of Southampton

